
The website is being upgraded......

The website is being upgraded......

always adhere to the customer-centric, through customized solutions and products to create value for customers; Build a win-win ecosystem with suppliers, partners and customers to promote audio and video technology progress and industrial development!
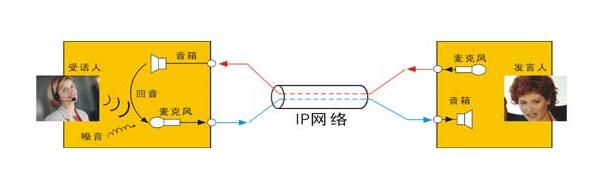
When a user is on the phone, if they hear their own voice being repeated in the receiver, it means there is an echo. An echo is actually your own voice "leaking" into your receiving path. This phenomenon occurs in any communication system, and in video conferencing systems, echoes produce this phenomenon more seriously.
In any communication conference, there are at least two nodes. From the point of view of each node, each call consists of two voice paths:
the sending path - locally picking up the voice and remotely playing back the voice. That is, from the mouth of the caller to the ear of the receiver.
Receiving path: Sounds are picked up remotely and played back locally. In other words, the receiver creates the receiving path when receiving the session, and the sender's voice is heard by the receiver's ear.
Figure 1 shows A simple voice call display between room A and Room B. From the perspective of room A, the transmission path sends the speech signal from room A to the ear of the listener in room B, and the receiving path sends the sound from room B back to the ear of the listener in Room A.
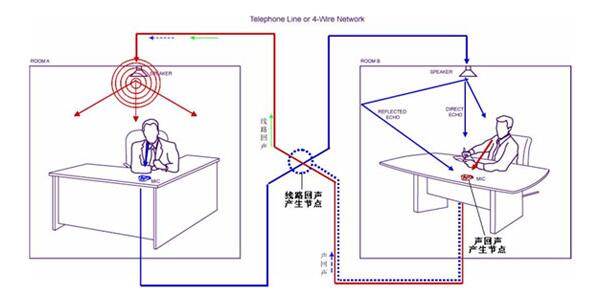
We know that the echo is due to the leakage of one's own speech sound into one's own receiving loop. In general, the echo phenomenon caused by leakage from the sending end to the receiving end can be generated in two ways:
* line echo - the echo generated by the coupling of the node device to the sending/receiving signal in the communication loop. The node devices that may generate echoes include audio mixing converters, telephone sets, video conference terminals, routers, and PBX telephone switches.
* Acoustic echo - the effect of the echo caused by the speaker coupling directly to the microphone through the air as the transmission medium.
Volume and delay: If the difference between the echo and the original signal is less than 50 milliseconds, the human ear generally does not feel the echo. It feels like the original signal has been enhanced. In addition, the reverberation time is longer in the general field. If the system leakage echo signal is more than 30dB lower than the original signal, and the delay is less than 80 milliseconds. The echo signal is usually drowned out by the reverberation sound, and the user cannot hear the echo.
* The louder the echo (the larger the amplitude of the echo), the more annoying it is.
* The greater the echo delay (the longer the speech round-trip delay), the more annoying it is.
* Seriously affected the clarity of the meeting.
* Multi-point echoes can easily cause inter-network sound oscillations.
The principle of echo cancellation::
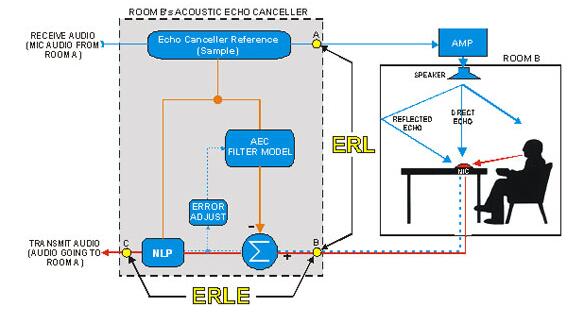
Suppose we want to eliminate the echo that room A can hear. We send the sound of the transmitting loop in room A to the Echo Canceller Reference for sampling, after which the sample is sent to the echo suppression model circuit for echo suppression model construction. This echo suppression model is then fed into the echo comparator on the receiving echo for comparison. Finally, the effect of echo suppression is achieved.
1. An important parameter of the echo sampling circuit is the coverage time of the echo canceller, which determines the maximum echo cancellation delay time, that is, how long the delay can be eliminated after the return of the echo. This time can be the network delay, or it can be the speed delay of the sound wave as it travels through the air. Once the echo delay time exceeds the echo canceller's coverage time, any echo canceller is useless.
2.Another important parameter is the intensity of the echo, the intensity of the echo signal must be lower than the intensity of the original voice signal. Once the echo signal is higher than the strength of the original signal, the echo cancellation circuit will also lose its function. Because at this point the system can't tell which signal should be an echo.
3. If the sound wave leaks from the speaker to the microphone through the air as the medium, the echo canceller with the above two characteristics alone cannot completely eliminate the echo. Because when sound waves travel through the air, the waveform will change greatly. Therefore, echo cancellation is more accurately described as similarity comparison. The NLP circuit equipped in the echo suppressor can provide the similarity level of multiple echo cancellation comparisons, which ensures that the echo suppressor can cancel the echo more accurately.
4.The echo canceller should be installed on both sides to eliminate both sides, if only a remote installation, then only 1 end of the echo can be eliminated.
1. Local echo canceller (represented by the built-in echo canceller in the CISCO system) : The echo canceller circuit is built in the local communication terminal to eliminate remote echo effects in the local conference.
Practical effect: For personal conversations in the form of headphones and earphones, the echo cancellation effect is obvious. For large venues using speakers and microphones, the sound echo can not be completely eliminated.
There are two main reasons: the delay time of echo cancellation which needs to be considered by the echo canceller includes the sum of the sonic velocity delay and the network delay, and the network delay is difficult to determine and often exceeds the coverage time of echo cancellation, resulting in the failure of the rebound effect; CISCO echo cancellation circuit does not provide NLP circuit, can not cope with the space of the echo signal variety.
Actual effect: can effectively achieve sound echo cancellation and line echo cancellation, echo cancellation effect is very obvious.
The main reason is that between the sampling circuit and the echo cancellation circuit, there is only a delay in the speed of the sound wave in the air, and the size of this delay is determined by the actual time used for the distance from the speaker to the microphone. Generally, the delay of 500 to 1000 people is only about 100 milliseconds. Conventional echo cancellers have a coverage time well beyond that. Therefore, there is no phenomenon that the echo cannot be eliminated normally due to the long delay time of the echo. Taking into account the changes in the transmission of sound waves in the air, an NLP circuit is added to the echo canceller to recognize the echo signal with different degrees of change.
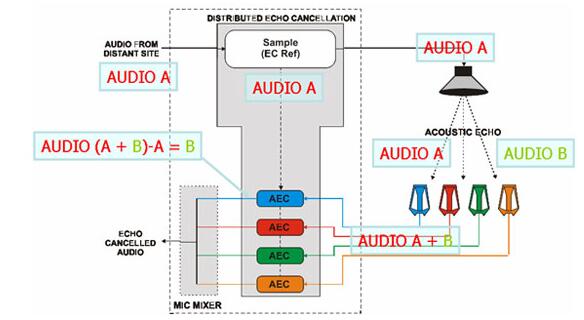
We mentioned earlier that as sound waves travel through the air, there are many changes in the waveform of the signal. When multiple microphones are used to pick up echoes, the echo size and waveform entering each microphone are different. Therefore, we use only one echo cancellation model to eliminate the different echoes produced by multiple microphones is completely unable to eliminate the echo. The distributed echo cancellation technique sets up different echo suppression models for each microphone to effectively suppress the echoes picked up by different microphones. Typical products include the Symetrix Radius NX 12×8 AEC-1 and ClearOne XAP800 digital audio processors.